Differences vs EVM
This document summarizes the differences you might encounter between building on Flow vs. other blockchains, especially Ethereum. This will be most useful to developers who are already familiar with building on a blockchain system. Check out Why Flow for a more beginner-friendly overview of the Flow blockchain.
The Flow Account Model
Key pairs establish ownership on blockchains. In other blockchains (e.g. Bitcoin), the user’s address is also calculated based on their public key, making a unique one-to-one relationship between accounts (addresses) and public keys. This also means there is no concrete “account creation” process other than generating a valid key pair. With the advent of smart contracts, Ethereum introduced a new account type for deploying contracts that can use storage space (i.e., to store contract bytecode). You can learn more about the distinction between EOA and Contract accounts on Ethereum here.
Flow combines the concepts of EOAs and Contract Accounts into a single account model and decouples accounts and public keys. Flow accounts are associated with one or more public keys of varying weights that specify interested parties that need to produce valid cryptographic signatures for each transaction authorized by that account.
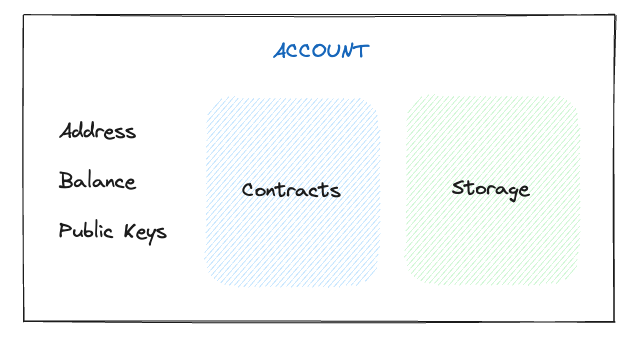
This natively enables interesting use cases, like key revocation, rotation, and multi-signature transactions. All Flow accounts can use network storage (e.g., for deploying contracts and storing resources like NFTs) based on the number of FLOW tokens they hold.
You must run an explicit account creation transaction on Flow to create a new account. Flow CLI can create an account on any network with a given public key.
Check out the Accounts concept document to learn more about Flow accounts.
Smart Contracts
On Flow, smart contracts are written in Cadence. Cadence syntax is user-friendly and inspired by modern languages like Swift. Notable features of Cadence that make it unique and the key power of the Flow blockchain are:
- Resource-oriented: Cadence introduces a new type called Resources. Resources enable onchain representation of digital assets natively and securely. Resources can only exist in one location at a time and are strictly controlled by the execution environment to avoid common mishandling mistakes. Each resource has a unique
uuidassociated with it on the blockchain. Examples of usage are fungible tokens, NFTs, or any custom data structure representing a real-world asset. Check out Resources to learn more. - Capability-based: Cadence offers a Capability-based Security model. This also enables the use of Resources as structures to build access control. Capabilities and Entitlements can provide fine-grained access to the underlying objects for better security. For example, when users list an NFT on a Flow marketplace, they create a new Capability to the stored NFT in their account so the buyer can withdraw the asset when they provide the tokens. Check out Capability-based Access Control to learn more about Capabilities on Cadence.
Cadence is not compiled. All contracts are open source on Flow.
Check out the Cadence website to learn more about Cadence.
If you are a Solidity developer, it's recommended to read Cadence's Guide for Solidity Developers to dive deeper into the differences between the two languages. Here are some additional resources that can help you get started with Cadence:
- The Cadence tutorial
- ERC-20 equivalent on Flow is the Flow Fungible Token Standard
- ERC-721 equivalent on Flow is the Flow Non-Fungible Token Standard
- Asset marketplaces with Cadence
- Tutorial
- NFT Storefront is an example marketplace standard
Transactions and Scripts
You can interact with the state on most other blockchains by cryptographically authorizing smart contract function calls. On Flow, transactions are more complex and are pieces of Cadence code. This means that any number of contracts and function calls can be composed together atomically to mutate the blockchain state.
Here is a sample transaction that mints an NFT from ExampleNFT contract on Testnet:
_47import NonFungibleToken from 0x631e88ae7f1d7c20_47import ExampleNFT from 0x2bd9d8989a3352a1_47_47/// Mints a new ExampleNFT into recipient's account_47_47transaction(recipient: Address) {_47_47 /// Reference to the receiver's collection_47 let recipientCollectionRef: &{NonFungibleToken.Collection}_47_47 /// Previous NFT ID before the transaction executes_47 let mintingIDBefore: UInt64_47_47 prepare(signer: &Account) {_47_47 self.mintingIDBefore = ExampleNFT.totalSupply_47_47 // Borrow the recipient's public NFT collection reference_47 self.recipientCollectionRef = getAccount(recipient)_47 .capabilities.get<&{NonFungibleToken.Collection}>(ExampleNFT.CollectionPublicPath)_47 .borrow()_47 ?? panic("The recipient does not have a NonFungibleToken Receiver at "_47 .concat(ExampleNFT.CollectionPublicPath.toString())_47 .concat(" that is capable of receiving an NFT.")_47 .concat("The recipient must initialize their account with this collection and receiver first!"))_47_47 }_47_47 execute {_47_47 let currentIDString = self.mintingIDBefore.toString()_47_47 // Mint the NFT and deposit it to the recipient's collection_47 ExampleNFT.mintNFT(_47 recipient: self.recipientCollectionRef,_47 name: "Example NFT #".concat(currentIDString),_47 description: "Example description for #".concat(currentIDString),_47 thumbnail: "https://robohash.org/".concat(currentIDString),_47 royalties: []_47 )_47 }_47_47 post {_47 self.recipientCollectionRef.getIDs().contains(self.mintingIDBefore): "The next NFT ID should have been minted and delivered"_47 ExampleNFT.totalSupply == self.mintingIDBefore + 1: "The total supply should have been increased by 1"_47 }_47}
Authorizing transactions is also more complex on Flow involving multiple roles:
- Accounts can have multiple keys with varying weights
- Multiple accounts can sign a single transaction (
preparetakes any number of arguments) - Transaction computation fees can be paid by a different account, called the
Payeraccount. - The transaction nonce is provided by the
Proposeraccount. This enables rate control and order to be dictated by a different party if needed. - All of the above roles can be the same account.
The same powerful concept also exists for querying the blockchain state using Scripts. Here is a sample script that fetches the ExampleNFT IDs owned by a given account on Testnet:
_21/// Script to get NFT IDs in an account's collection_21_21import NonFungibleToken from 0x631e88ae7f1d7c20_21import ExampleNFT from 0x2bd9d8989a3352a1_21_21access(all) fun main(address: Address, collectionPublicPath: PublicPath): [UInt64] {_21_21 let account = getAccount(address)_21_21 let collectionRef = account_21 .capabilities.get<&{NonFungibleToken.Collection}>(collectionPublicPath)_21 .borrow()_21 ?? panic("The account with address "_21 .concat(address.toString())_21 .concat("does not have a NonFungibleToken Collection at "_21 .concat(ExampleNFT.CollectionPublicPath.toString())_21 .concat(". The account must initialize their account with this collection first!")))_21_21 return collectionRef.getIDs()_21_21}
Check out Transactions and Scripts to learn more about the concepts. You can also read the Cadence language reference on Transactions to dive deeper.
Flow Nodes
Developers need a blockchain node to send transactions and fetch state. Flow is based on a multi-node architecture that separates roles like consensus and computation. You can learn more about the Flow architecture here.
Access Nodes are the node type that are most useful for developers, as they provide access to the Flow network via an API.
SDKs and Tools
If you’re already familiar with blockchain development, here's a comparison between popular software packages and Flow's tooling:
- hardhat / Truffle / Foundry
- Flow CLI provides local development tools and the Flow Emulator
- OpenZeppelin
- go-ethereum
- Flow Go SDK
- FCL also provides Backend API for Flow in JS
- web3.js
- FCL
- flow-cadut provides more utilities for using Flow on Web
- Remix
- Flow Playground provides basic experimentation on the web
- Cadence VSCode Extension is strongly suggested to install for local development
- Testing Smart Contracts
- Cadence testing framework enables native tests in Cadence.
- overflow for testing in Go.
- js-testing for testing in JS.